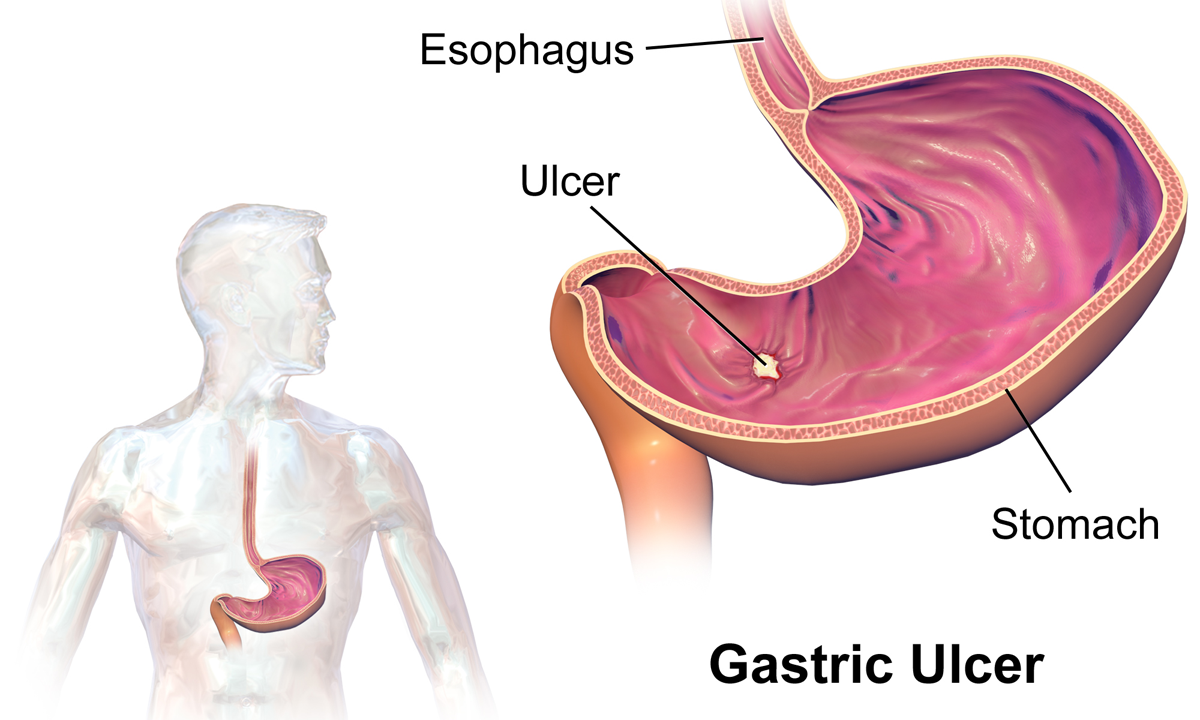
food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome wiki
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE cell-mediated food allergy commonly diagnosed in infants and young children. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a severe systemic response to food protein that typically occurs 1 to 4 hours after the ingestion of the causative.
Food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome wiki Sunday May 29 2022 Edit The acute form of hepatitis generally caused by viral infection is characterized by constitutional.

. The primary symptom is profuse repetitive vomiting. The child may appear. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES sometimes referred to as a delayed food allergy is a severe condition causing vomiting and diarrhea.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE cell-mediated food allergy commonly diagnosed in infants and young children. The expression of food protein allergy in man is very heterogeneous varies with the age of the subject and is to a certain extent genetically determined. In recent years new-onset adult FPIES has.
It is much less common than IgE-mediated food allergy and typically occurs in babies. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a condition in children that can be considered to be a delayed form of food allergyUnlike typical food allergies symptoms. Typical symptoms of FPIES include severe vomiting diarrhea and.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-immunoglobin E IgE-mediated food hypersensitivity disorder that primarily affects formula. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a severe non IgE delayed form of food allergy. Acute FPIES reactions generally occur in children ages 412 months 14 hours after ingestion of the trigger food.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-immunoglobulin E IgE mediated gastrointestinal food hypersensitivity that manifests as profuse repetitive vomiting. In some cases symptoms can. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a systemic non IgE-mediated response to a specific trigger within food - most likely food proteinFPIES presents in two different.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-immunoglobulin E IgE mediated gastrointestinal food hypersensitivity that manifests as. Acute food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated allergy and is characterized by repetitive profuse vomiting episodes often in association with. The most common FPIES food triggers are cows milk soy rice and oats but any food can cause FPIES symptoms.
In recent years new-onset.

Fpies Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome

Fpies Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome

Fpies Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome

Fpies Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome
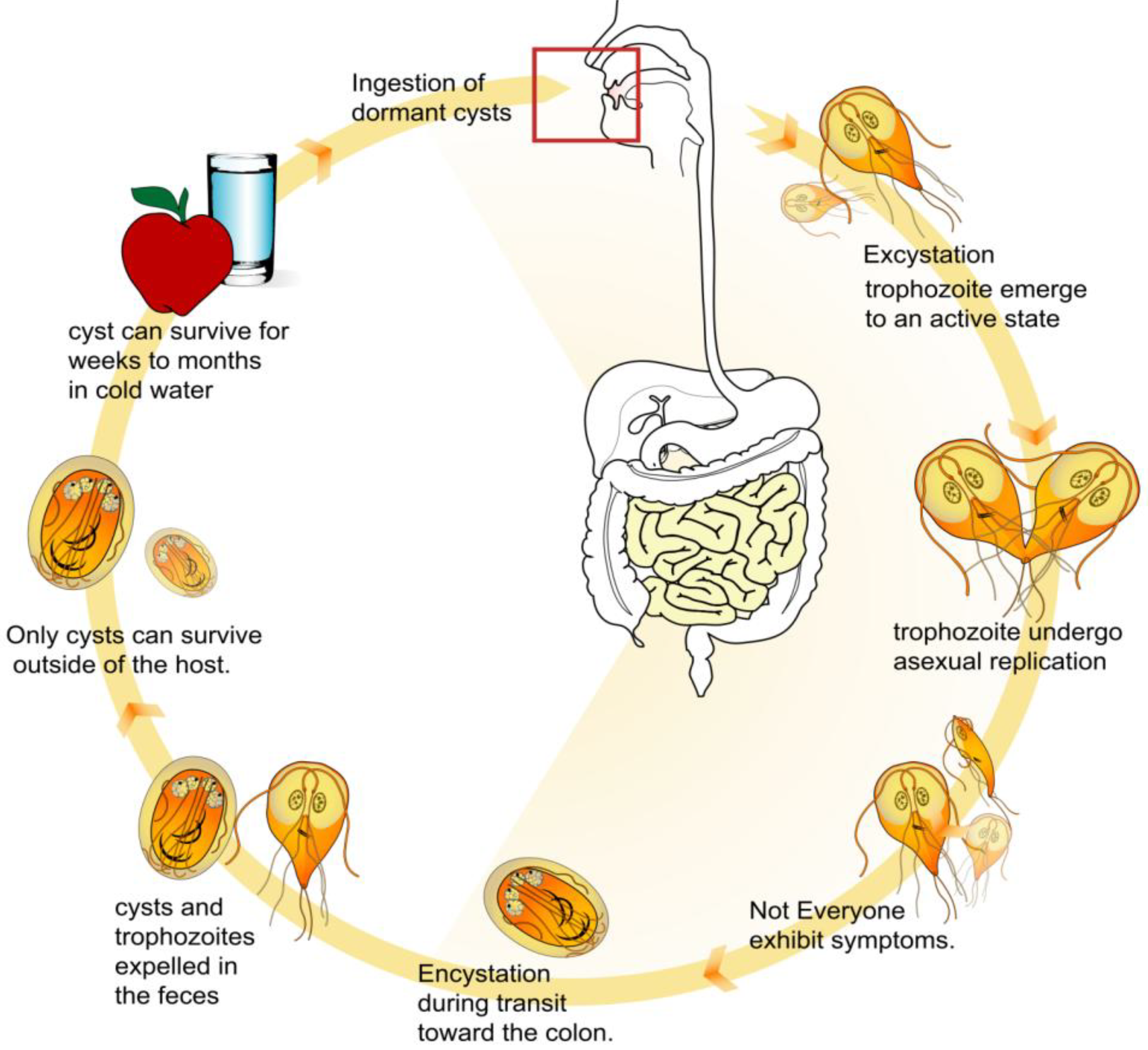
Ijerph Free Full Text Water Related Parasitic Diseases In China Html

Fpies Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome
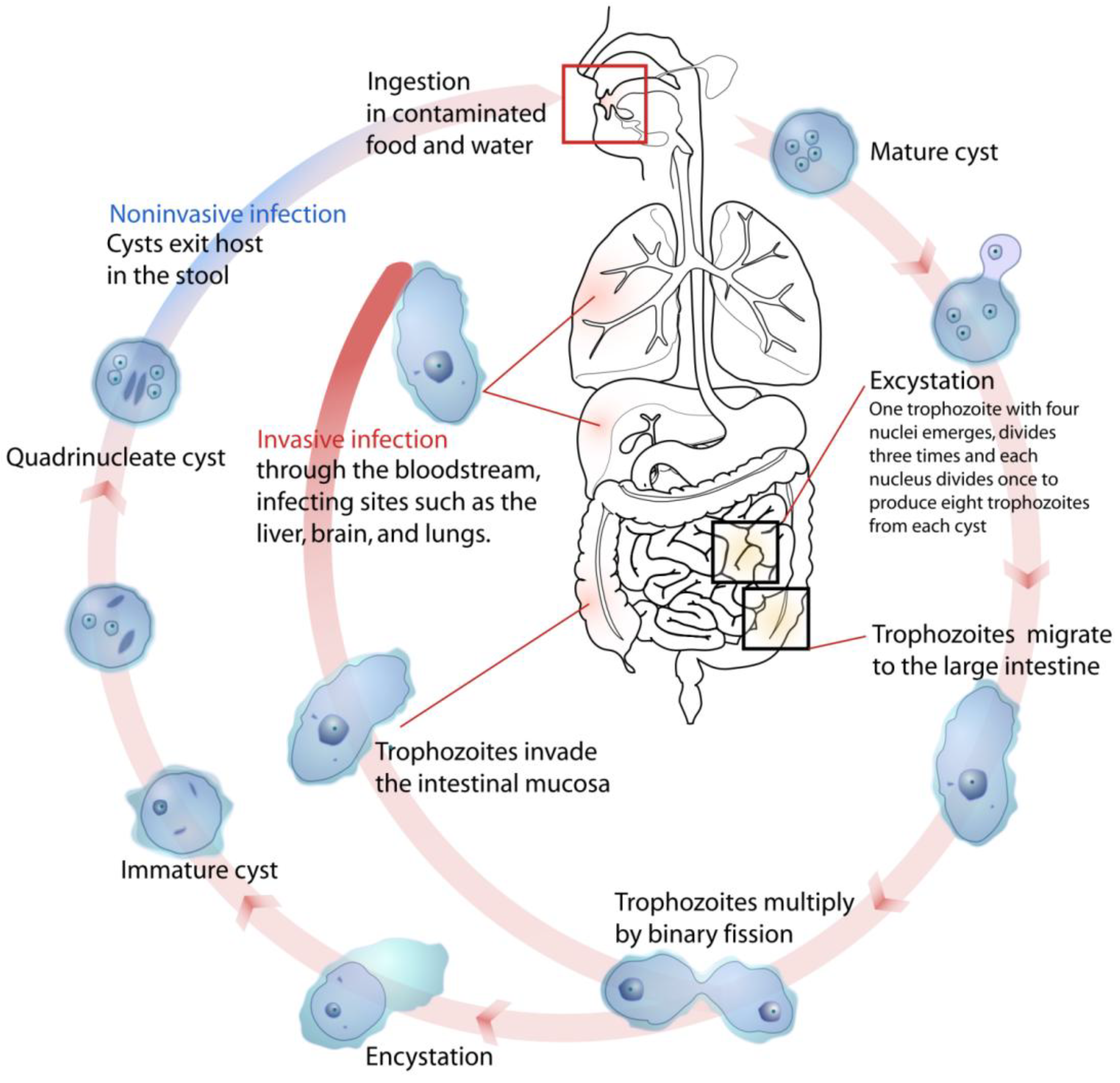
Ijerph Free Full Text Water Related Parasitic Diseases In China Html

Fpies In A Mother S Eye Neocate

Fpies Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome